Brain drain involves the substantial emigration of skilled individuals from a country or organization, often in pursuit of better opportunities elsewhere.
Brain drain manifests at different levels, from the geographic to the organizational or industrial. That is, professionals may leave one country or region for better prospects, or workers may seek better pay, benefits, or career advancement in another company or industry. Common triggers include political instability, poor quality of life, limited access to healthcare, and a lack of economic opportunities. The effects of brain drain are profound, also leading to a loss of tax revenue and stunted economic growth.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
What is Brain Drain?
Brain drain, a term deeply ingrained in the discourse of global migration, signifies the emigration of educated or skilled individuals from one country, sector, or field to another. Furthermore, this movement is often driven by the pursuit of better pay or living conditions. It has become a critical concern for many developing nations, as they face challenges in retaining their most valuable human capital.
Merriam-Webster defines brain drain as “the departure of educated or professional people from one country, economic sector, or field for another, usually for better pay or living conditions”. Hence, this definition highlights several key aspects. It underscores the substantial emigration involved, often triggered by political turmoil or the allure of better opportunities elsewhere. It also emphasizes the detrimental loss of human capital, which can severely impact the local economy.
The complexity of brain drain has grown, with nations struggling to retain their elite talent. As a result, they must create environments that can compete with the professional opportunities and higher standards of living found elsewhere.
Types of Brain Drain
Geographic Brain Drain
Firstly, Geographic brain drain occurs when skilled professionals leave their home country or region for better opportunities. Moreover, this phenomenon is common among talented individuals from developing nations. They migrate to more developed economies, seeking higher salaries, better living standards, and access to advanced resources and technologies.
Organizational Brain Drain
Secondly, Organizational brain drain involves the mass exodus of skilled workers from a particular company or organization. It often results from a lack of growth opportunities, job stability, or competitive compensation. Therefore, employees then seek employment elsewhere, frequently with rival firms or in different industries.
Industrial Brain Drain
Finally, Industrial brain drain occurs when talented individuals leave an entire industry. This is usually due to technological or societal changes that the industry cannot adapt to. Such brain drain also significantly impacts the industry’s competitiveness and innovation, as it loses its most skilled and knowledgeable workers.
Causes of Brain Drain
Economic Opportunities
Brain drain can be attributed to a variety of factors. Economic opportunities such as higher salaries, better living standards, and access to advanced healthcare and housing are often the primary drivers of brain drain. Many developing nations, such as Pakistan, have struggled to retain their highly skilled professionals, who are drawn to the promise of more prosperous careers abroad.
Political Reasons
Aside from economic factors, political instability and persecution based on religion, gender, or sexuality can also contribute to brain drain. When individuals feel unsafe or discriminated against in their home countries, they may also seek refuge and opportunities elsewhere. This loss of talent can be particularly devastating for developing countries, as they often lack the resources to adequately support and retain their skilled workforce.
Technological Changes
Additionally, technological change can be a cause of brain drain, as automation and digitization disrupt traditional industries and lead to job losses, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing and clerical work. Skilled workers may then choose to relocate to regions with more promising economic opportunities and technological advancements.
| Causes of Brain Drain | Examples |
|---|---|
| Economic opportunities | Higher salaries, better living standards, access to advanced healthcare and housing |
| Political instability | Conflict, civil unrest, government repression |
| Persecution | Discrimination based on religion, gender, or sexuality |
| Technological change | Automation and digitization disrupting traditional industries |
Addressing the causes of brain drain requires a multifaceted approach, including improving economic opportunities, ensuring political stability, and fostering an environment that values and retains skilled professionals. Governments and policymakers must work towards creating a more attractive and sustainable ecosystem for their talented citizens to thrive and contribute to the growth and development of their home countries.
Effects of Brain Drain
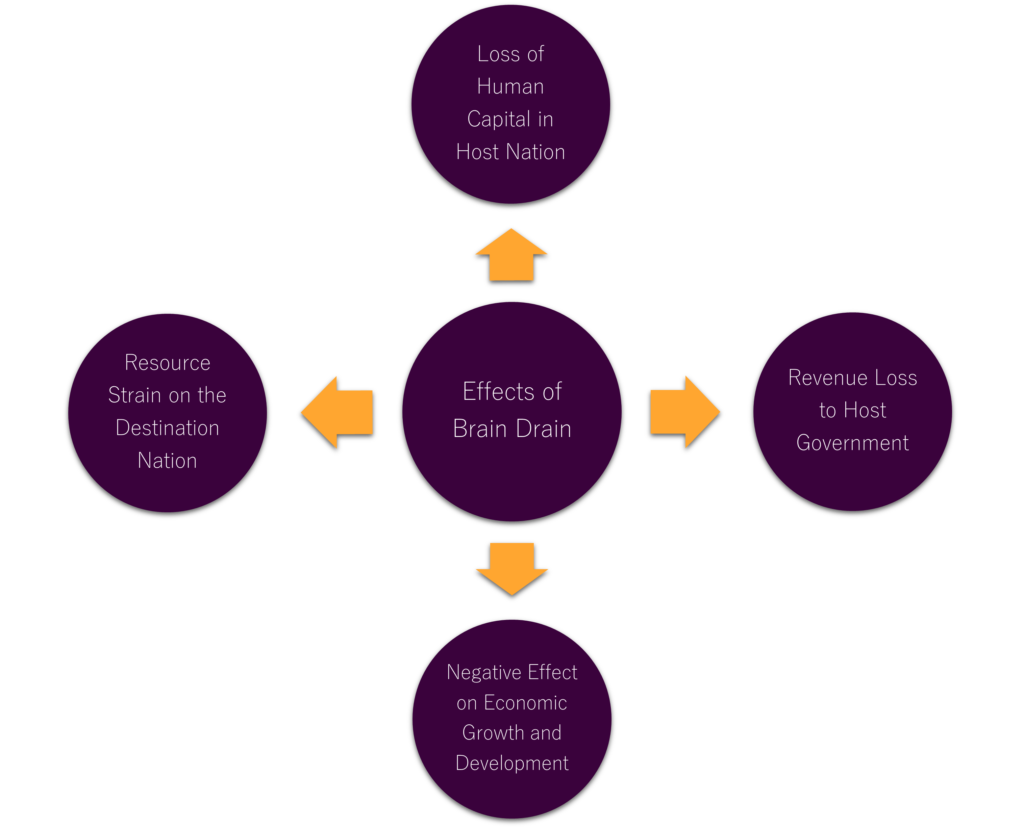
Brain drain has profound impacts on both the source and destination regions. It results in a notable human capital loss, reducing the number of highly educated and trained individuals in their countries of origin.
The repercussions of brain drain transcend mere human resource depletion. Governments suffer from revenue loss due to the absence of tax contributions from these emigrated experts. Moreover, this financial burden can severely impede efforts towards economic growth and development in the affected areas.
Furthermore, the resource strain on the destination regions is considerable. The influx of skilled workers can overwhelm critical services and infrastructure, leading to increased costs and potential shortages. This scenario can stifle the development of the host regions as well.
To counteract the effects of brain drain, governments and policymakers must implement comprehensive strategies. These should address the root causes, including political instability, limited healthcare access, and economic opportunity shortages. Investing in the economy, offering competitive wages, legal and social reforms, and enhancing access to essential services can aid in retaining skilled professionals. This approach further fosters sustainable development.
Case study: Brain Drain and Pakistan
Pakistan has faced a severe brain drain, with many skilled professionals leaving for better opportunities abroad. In 2021, about 225,000 Pakistanis departed, increasing to 765,000 in 2022 (Source: Tribune).
Causes and Implications of Brain Drain in Pakistan
The main causes of brain drain in Pakistan include low economic opportunities, wages, working conditions, infrastructure, technology access, and high political instability. These factors have led to the loss of doctors, engineers, and IT experts.
The brain drain has further resulted in a shortage of skilled workers, reduced investment in education, and a decline in innovation. It has also worsened economic inequality and impacted academic institutions and healthcare.
Additionally, the devaluation of the Pakistani currency has made supporting children studying abroad increasingly difficult. Many international students from Pakistan choose to stay in their host countries due to economic uncertainties.
| Period | Number of Pakistanis who Migrated | Highly Qualified Professionals | Highly Skilled Professionals | Skilled Professionals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Since 1971 | 6,019,888 | 4.18% | 7.55% | 88.27% |
The brain drain has significantly impacted sectors like academia, healthcare, and research productivity. One in three medical students in Pakistan plan to migrate due to resource shortages and mismanagement.
The brain drain issue in Pakistan is a pressing concern, affecting the country’s economic and social development. Hence, addressing the root causes and implementing measures to retain skilled professionals is crucial for Pakistan’s prosperity.
Measures to Reduce Brain Drain
Combatting brain drain necessitates a comprehensive strategy. Governments and entities must adopt diverse tactics to retain and draw in skilled professionals. This includes enhancing working environments, elevating compensation, investing in pivotal sectors, and offering specific incentives.
Improving working conditions and increasing salaries are pivotal in retaining top talent. Governments must concentrate on enhancing governance, fortifying institutions, and improving public service delivery to tackle the core reasons behind persistent emigration. Moreover, extending benefits beyond mere salary, such as health insurance, can significantly boost retention rates and counteract brain drain.
Investment in sectors like healthcare, education, and technology can also generate more opportunities for skilled workers. This signals a dedication to their professional advancement. Offering tax incentives to returning emigrants can encourage the return of high-skilled individuals and aid in economic development in their home countries.
Through these strategies, nations and entities can strive to retain and attract the skilled professionals essential for their success and sustainable economic expansion.
| Measure | Impact |
|---|---|
| Improving working conditions and raising salaries | Enhances retention of skilled professionals |
| Investing in key industries like healthcare, education, and technology | Creates more job opportunities for skilled workers and signals commitment to their professional development |
| Providing incentives, such as tax breaks and housing subsidies | Encourages the return of high-skilled individuals and supports economic development |
| Improving the business environment to attract foreign investment | Generates more job opportunities for skilled professionals |
Conclusion
Brain drain is a complex issue, affecting many nations, especially in the developing world. The loss of skilled professionals hampers economic growth and weakens the social fabric of their communities. This phenomenon has far-reaching consequences, impacting both the economy and society.
There is no single solution to brain drain, but a comprehensive approach can be effective. Improving working conditions, increasing salaries, and investing in key sectors are crucial steps. Additionally, offering incentives and creating a welcoming business environment can attract and retain talent. By addressing the push and pull factors, nations can maximize their human capital and achieve sustained economic and social progress.
The battle against brain drain requires a collaborative effort from policymakers, businesses, academia, and civil society. By focusing on retaining talent and fostering development, countries can unlock the potential of their skilled workforce.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
This website contains affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission at no additional cost to you.


