Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling method for gathering data from specific subgroups of a population. This approach involves selecting participants based on predetermined characteristics, such as age, gender, or occupation. As a result, it is invaluable for gathering insights from diverse groups efficiently. By setting quotas for each subgroup, researchers can further achieve a balance that reflects the broader population. Hence, this makes it easier to analyze and generalize findings using various sampling methods.
Quota sampling aims to have the final sample mirror the population’s characteristics. The process involves dividing the population into subgroups, determining proportions, selecting observations based on proportions, and ensuring the representativeness of the sample. It is used when researchers want to study specific subgroups or relationships between them.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
What is Quota Sampling?
Quota sampling is a non-probability sampling technique. It also involves selecting participants based on predetermined characteristics. Researchers set quotas for different subgroups within a population, such as age, gender, or occupation. Therefore, this method aims to achieve the best representation of respondents in the final sample, with estimates being more representative.
In quota sampling, researchers divide the sample population into subgroups and determine the weightage of subgroups. Further, they select an appropriate sample size and conduct surveys according to the defined quotas. This technique is often used in market research when specific subgroup representation is essential. As a result, the key components of quota sampling include:
- Dividing the sample population into subgroups
- Determining the weightage of subgroups
- Selecting an appropriate sample size
- Conducting surveys according to the defined quotas, which is a critical step in survey sampling and quantitative research methodology
Quota sampling is a cost-effective and useful method when time is limited or specific criteria need to be met in research. This ensures an accurate representation of the population of interest.
The Process of Implementing Quota Sampling
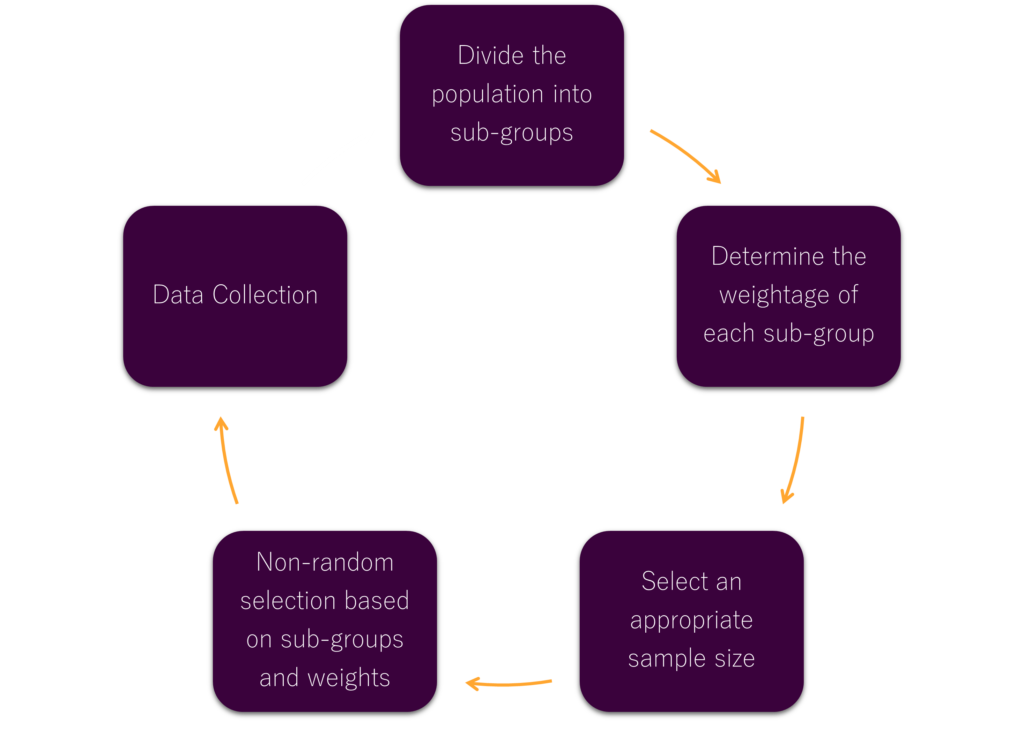
Quota sampling’s implementation requires several steps. These include dividing the population into subgroups, determining the sample size, and assigning weights to each subgroup. This method is essential for ensuring the sample mirrors the population, facilitating precise statistical analysis and dependable results.
Quota sampling’s core involves selecting subjects based on specific criteria like gender, age, and income. This strategy allows researchers to gather data from a representative sample, vital for drawing conclusions about the broader population. For example, a study on consumer preferences might use quota sampling to recruit participants based on age, income, and education, ensuring the sample accurately reflects the target demographic.
Moreover, assigning weights to subgroups is another critical aspect of quota sampling. This ensures the sample’s proportionality to the population, also enabling accurate statistical analysis and reliable findings.
To illustrate quota sampling’s implementation, consider the following:
- Divide the population into subgroups based on specific criteria, such as age, income, and education level.
- Select an appropriate sample size, such as 500 participants.
- Determine the weightage of subgroups, such as 25% for high-income and 30% for medium-income participants, to maintain proportionality.
- Using the assigned weights to select participants from each subgroup.
Applications of Quota Sampling
Quota sampling is a versatile tool, applied in various sectors such as market research, social sciences, and business and consumer studies. Its applications span several domains:
- Market research: It facilitates the collection of data on customer preferences and buying behaviours, employing quota methods to deepen the understanding based on different consumer characteristics.
- Social science studies: It is utilized to study the attitudes and behaviours of various groups.
- Business and consumer research: It aids in gathering data on customer behaviour, such as gender-based spending habits, to inform strategies that cater to diverse customer needs.
Hence, through quota sampling, researchers can attain a profound comprehension of their target audience.
Advantages and Limitations of Quota Sampling
Quota sampling is a valuable technique in quantitative research methodology, enabling researchers to obtain a representative sample by dividing the population into subgroups based on different characteristics. This method is also highly beneficial in survey sampling, ensuring a proportional representation of specific demographic groups in the sample. However, quota sampling also faces limitations, including the risk of bias and the challenge of generalizing to the broader population.
The advantages of quota sampling include its ability to provide a representative sample, its efficiency, and its cost-effectiveness. It also allows researchers to ensure key subgroups within the population are adequately represented in the sample. Despite these benefits, the method has drawbacks, such as the risk of sampling bias and the challenge of accurately representing population characteristics. To address these challenges, researchers can employ strategies like stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and weighting in their statistical analysis.
Benefits for Researchers
Quota sampling offers several benefits for researchers, including time-saving, cost reduction, and flexibility. It is also convenient for data analysis and interpretation, making it a popular choice in market research and social science studies. Further, quota sampling enables researchers to evaluate different effects by segregating the population into subgroups based on different backgrounds, gender, or other relevant factors.
Potential Drawbacks
Despite its advantages, quota sampling has some drawbacks, including limitations in projecting results to the entire population and susceptibility to bias if the researcher lacks experience. It may also not be suitable for studies that require detailed accuracy, as it does not involve random selection.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Representative sample | Potential for bias |
| Efficient and cost-effective | Lack of generalizability |
| Flexibility in sampling | Limited accuracy |
Conclusion
Quota sampling enables the acquisition of a representative sample from a population efficiently. It facilitates rapid, economical, and targeted data collection, allowing for the examination of specific demographic segments. This method also accelerates data gathering and diminishes survey expenses by precisely aligning samples with demographic objectives.
However, it is imperative to recognize the limitations and risks inherent in quota sampling. These include the risk of survey bias and the absence of random selection, potentially resulting in an inaccurate representation of the wider population. Hence, acknowledging these challenges empowers researchers to implement corrective measures, ensuring the optimal utilization of quota sampling in their endeavours.
In summary, it offers a dependable and efficient means to collect data and derive insightful information. Therefore, by integrating quota sampling into their research methodologies, researchers can enhance their decision-making processes and fulfil their objectives.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
This website contains affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission at no additional cost to you.


