Simple random sampling stands out as a key method to ensure the representativeness of samples. This technique involves selecting a sample from a population where every member has an equal chance of being chosen. Hence, it is one of the most important probability sampling methods.
Simple random sampling is vital in various disciplines, such as social sciences, medicine, and marketing. It also helps researchers avoid bias and ensures their samples accurately reflect the population. As a result, simple random sampling is a fundamental aspect of statistical research, essential for making accurate predictions and informed decisions.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
What is Simple Random Sampling?
Simple random sampling falls under probability sampling, ensuring every population member has an equal chance of selection. Furthermore, the aim is to diminish bias and ensure the sample mirrors the population. This also boosts research validity.
Simple random sampling stands out for its error-minimizing capabilities and truthful population representation. Through probability sampling, researchers can eliminate bias, ensuring their sample accurately reflects the population’s characteristics. This is critical in statistical research, where the precision of findings is essential.
Key Characteristics of Simple Random Sampling
Some key characteristics of simple random sampling include:
- Equal chance of selection: Every member of the population has an equal opportunity to be selected for the sample.
- Randomness: The selection process is random, reducing the risk of bias and ensuring that the sample is representative of the population.
- Representativeness: The sample is representative of the population, allowing researchers to generalize their findings to the larger population.
Hence, this technique is indispensable in statistical research, applied across various disciplines like social sciences and economics.
The Process of Simple Random Sampling
To execute simple random sampling, researchers adhere to a series of steps. The process can be outlined as follows:
- Define the population: Identify the group from which the sample will be drawn.
- Determine the sample size: Decide on the number of individuals to include in the sample.
- Use a randomization technique: Employ a method, such as a random number generator, to select the sample from the population.
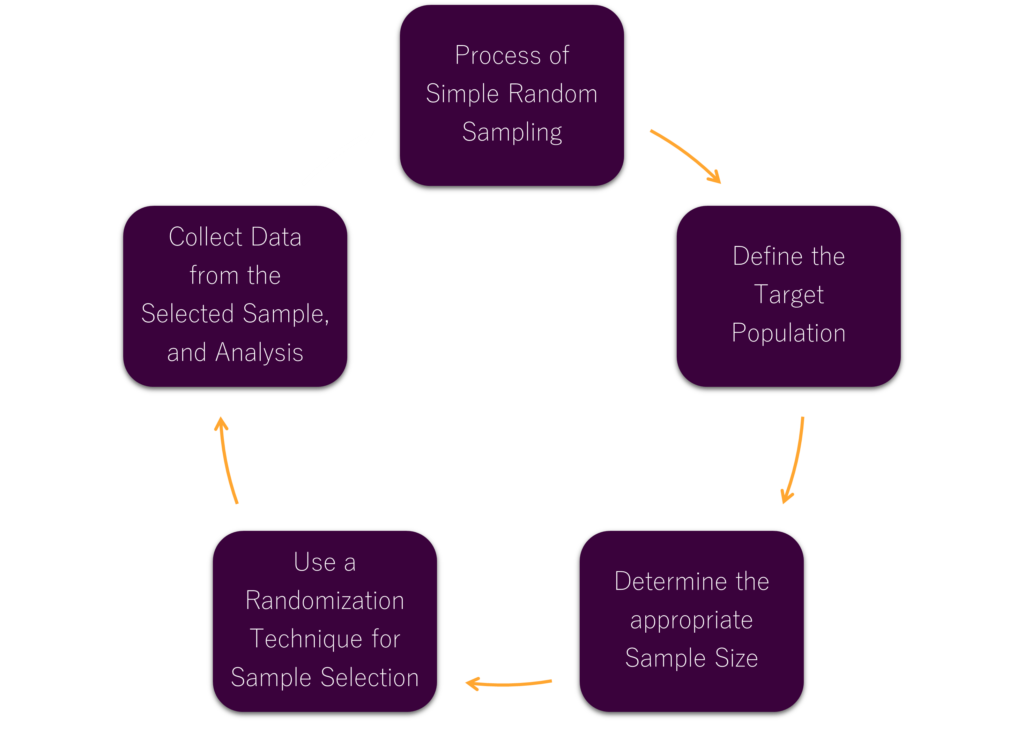
By adhering to these steps and utilizing a simple random sampling technique, researchers can further minimize bias. This also ensures their sample is representative of the population. Moreover, such representation is vital for drawing accurate conclusions from the data collected.
Essential Tools and Technologies for Random Sampling
Simple random sampling heavily relies on various tools and technologies. That is, effective research methodology employs specialized tools for generating random samples, managing data, and analyzing results.
Random Number Generators
Firstly, random number generators are indispensable for creating random samples in research methodology. They are used to select participants or data points randomly, hence, minimizing bias in sampling methods.
Statistical Software Solutions
Statistical software solutions, such as R or SPSS, also offer a plethora of tools and features for sampling methods. These software solutions enable the generation of random samples, data analysis, and result visualization, making them vital for research methodology.
Manual Selection Methods
Manual selection methods, like random sampling from a list, are also employed in simple random sampling. Therefore, these methods involve manually selecting participants or data points through a random process. While time-consuming, they are effective in specific research contexts.
Advantages and Limitations of Simple Random Sampling
Simple random sampling is a prevalent technique in research methodology, also boasting several advantages in probability sampling. Its primary benefit lies in its capacity to reduce bias, further ensuring the sample mirrors the population. This is critical in research, hence, enabling researchers to make precise inferences about the population.
Its simplicity and straightforward implementation make simple random sampling a favoured choice in research methodology. However, it has limitations, such as the challenge of achieving true randomness in certain populations. To mitigate these issues, researchers might explore alternative methods or employ techniques like stratified or cluster sampling.
Benefits in Research Studies
The advantages of simple random sampling in research studies include:
- Minimizing bias and ensuring representativeness
- Allowing for accurate conclusions to be drawn about the population
- Being a simple and easy-to-implement method
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenges encountered during sampling include:
- Random error: This can be mitigated by enlarging the sample size or adopting different sampling approaches.
- Difficulty in achieving truly random samples: Techniques such as stratified or cluster sampling can help overcome this hurdle.
| Sampling Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Random Sampling | Minimizes bias, easy to implement | Potential for random error, difficulty in achieving truly random samples |
| Stratified Sampling | Allows for more accurate representation of subgroups | Can be complex to implement, and requires prior knowledge of subgroups |
| Cluster Sampling | Can be more efficient than simple random sampling, reduces costs | May introduce bias, requires careful selection of clusters |
Real-World Applications
Simple random sampling is also prevalent across diverse sectors, including market research, social sciences, and medical research. This is because it guarantees that every individual within the population has an equal probability of being chosen. As a result, this leads to a sample that accurately represents the broader population.
- Market research: simple random sampling is also used for collecting insights into consumer behaviour and preferences. For instance, a company might employ this method to assemble a group of customers for a survey on a new product launch.
- Medical research: This technique is employed to recruit participants for clinical trials, hence, ensuring the sample mirrors the population’s demographics.
- Social sciences: It is also utilized in sociological and psychological studies to gather data on social issues and behaviours.
The application of simple random sampling in these domains enhances the trustworthiness and accuracy of research outcomes. As a result, it aids in shaping informed decisions and policy formulations.
Conclusion
Simple random sampling is instrumental in ensuring the reliability and validity of research outcomes. By randomly selecting participants or units from a population, this technique also effectively eliminates bias. Moreover, it almost guarantees that the sample accurately represents the larger group.
To further enhance the efficacy of simple random sampling, determining the appropriate sample size is critical. Employing advanced random number generation techniques is also essential. By following these best practices, researchers can harness the full power of this method. They can draw accurate conclusions and uncover significant insights, contributing to the advancement of their fields. In conclusion, simple random sampling remains a fundamental aspect of research methodology as it empowers researchers to make informed decisions.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
This website contains affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission at no additional cost to you.


