In 2021, U.S. multinational corporations employed an astonishing 43.3 million workers worldwide. This fact highlights their significant impact and extensive global reach. These giants, also known as MNCs, are instrumental in the advancement of globalization by operating in numerous countries. They significantly influence the international economic scene. MNCs range from well-known brands like Apple and Microsoft to vast entities such as Walmart and ExxonMobil. Moreover, these entities are key players in the global economy.
The contribution of multinational corporations to local economies is generally positive. However, due to their huge presence, they also encounter numerous challenges. These include complexities in regulation, political instability, and navigating diverse cultural landscapes. Additionally, they must contend with the unpredictable nature of currency exchange rates. Despite these hurdles, these global companies, transnational enterprises, international conglomerates, and worldwide corporations significantly impact the international business environment. Their varied operational structures include both decentralized and centralized approaches.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
Defining Multinational Corporations
A multinational corporation (MNC) is a business spanning multiple countries, not just its place of origin. Through operations abroad, it makes income in foreign lands. These companies also serve as economic boosts where they expand. For investors, MNCs provide a path to worldwide markets in their portfolios.
What Is a Multinational Corporation?
Multinational corporations (MNCs) extend their reach beyond their home soil to produce goods or services internationally. Furthermore, Black’s Law Dictionary identifies such firms as MNCs if they earn a quarter or more of their money abroad. Giants like IBM, Apple, and Walmart also fall within this category. Then there’s Nestlé S.A., showcasing a transnational approach.
Key Characteristics of MNCs
MNCs boast an international network, operate in many tongues, and have complex structures. They make direct investments in overseas markets and further employment opportunities. MNCs aim for enhanced efficiency and lower costs while expanding their market share. They also contribute to the host countries’ treasuries. However, their presence can impact local businesses, often adversely.
Distinguishing MNCs from Domestic Companies
Making goods and selling them abroad doesn’t mean a company is an MNC. To be one, a company must also have a presence in different countries. By setting up factories in less developed nations, MNCs can further cut production costs by 70%. They also try to be close to their biggest markets to save on shipping and get quick customer feedback. The global spread and operations set MNCs apart from their domestic counterparts. While internationalization finds them new customer bases, it allows them tax benefits too. This advantage comes as countries vie for MNCs’ investment.
History and Evolution of Multinational Corporations
The origins of modern multinational corporations stretch back centuries. An example is the establishment of the British East India Company in 1600. This company engaged in international trade, and exploration, and maintained trading posts in India. Similarly, the Swedish Africa Company (1649) and the Hudson’s Bay Company (1670) are also early examples of MNCs. They played roles in trade and exploration in Africa and North America, respectively.
Early Multinational Enterprises
Initially, these entities were primarily chartered or trading companies. They ventured abroad, setting up trading posts, factories, and also colonies. The East India Company notably significantly influenced the British colonization of India. Moreover, the Swedish Africa Company and Hudson’s Bay Company were key in exploring and trading natural resources in Africa and North America.
Growth of MNCs in the 20th Century
In the 20th century, the rise of multinational corporations spiked. This was spurred by globalization and the development of transportation and communication. Also, the increase in international trade and investment was crucial. Presently, these corporations are vitally important in the global economy.
The course of multinational corporations’ growth features key shifts in industry control and power. For example, before the 1973 oil crisis, the Seven Sisters majorly influenced the petroleum sector. They controlled about 85% of the world’s reserves. Afterwards, the OPEC cartel and state-owned enterprises like Saudi Aramco, Gazprom, and the China National Petroleum Corporation rose in importance.
The “golden age of oil” and the dominance of Seven Sisters oil companies before 1973 boosted MNCs in energy. OPEC, a key oil production group, and U.S. actions in Iraq in 2003 further underlined MNCs’ global economic and political roles.
Types of Multinational Corporations
Multinational corporations (MNCs) vary significantly in their structure and approach. Knowing the distinct types is vital for manoeuvring the global business scene. To understand MNC diversity, we’ll delve into their primary categories.
Decentralized Corporation
Decentralized MNCs lack a central administrative hub, allowing quick expansion and local autonomy. Therefore, these entities enable subsidiaries to tailor strategies to specific market needs, enhancing agility and adaptability.
Centralized Global Corporation
On the flip side, centralized global firms have a single headquarters managing global ventures. They might outsource to cut expenses and establish operations worldwide for efficient resource use.
International Division of a Corporation
International MNCs harness their parent’s R&D to stay innovative and competitive locally. Hence, they often maintain a dedicated division overseeing global strategies and product adaptations for varied markets.
Transnational Corporation
Transnational entities span multiple countries with a decentralized model, aiming for local market insight and rapid response. For instance, Nestlé operates globally, making both HQ and field decisions.
Multinational corporations and Globalization
Multinational corporations (MNCs) are pivotal in the globalization process. They greatly influence worldwide trade through their broad international operations. These operations also allow them to participate in commerce across borders and investments. MNCs vary, from those with decentralized strategies to highly centralized entities, including global, international, and transnational corporations like IBM and Apple.
Impact of MNCs on Global Trade
MNCs are vital in knitting economies together, thanks to their far-reaching investments. They help link national markets, leading to a globally integrated economic system. This globalization has significantly boosted cross-border trade and investments, making national economies more interconnected than ever.
MNCs and Economic Integration
Companies such as Almarai and Nokia have skillfully tapped into globalization to expand their markets internationally. This allows goods and services to flow more freely between economies. Through globalization, MNCs can also meet local demands effectively, boosting their presence and customer loyalty. Additionally, this led to the formation of groups like the European Union (EU) and ASEAN, making the global economy even more integrated.
Role and Importance of Multinational Corporations
Multinational corporations (MNCs) play a significant role in the global economy by accessing global markets, achieving cost efficiency and competitiveness, and contributing to employment and economic growth in various countries.
Access to Global Markets
MNCs efficiently reach markets worldwide due to their international presence. This also allows them to reach new customers globally. They take advantage of economies of scale, thus cutting production and distribution costs, leading to competitive prices for consumers.
Cost Efficiency and Competitiveness
Operating in diverse countries, MNCs acquire materials at lower prices and access cheap labour. This strategy boosts their cost efficiency and overall competitiveness. They also enjoy the benefits of favourable tax and regulatory conditions, amplifying their capability to invest in growth and innovation.
Employment and Economic Growth
In 2021, U.S. MNCs provided jobs for 43.3 million people globally, highlighting their significant role in job creation. Hence, they contribute to economic growth by increasing efficiency, lowering prices, and providing local employment. MNCs also offer better salaries, attract local workers, and support the development of local economies.
Therefore, the impact of multinational corporations on the global economy is profound. Their strategies help drive economic growth and competition worldwide.
Disadvantages of MNCs
Multinational corporations offer many benefits, but they also have some downsides:
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal and Tax Compliance Burdens | MNCs face increased compliance requirements due to operating in multiple jurisdictions with different laws and regulations. |
| Public Relations Challenges | MNCs can face accusations of sending jobs overseas or exploiting local workers and resources. |
| Political and Economic Risks | MNCs can be exposed to risks in less developed or politically unstable countries. |
| Threat to Local Industries | MNC operations can threaten local industries in host nations, impacting economic development. |
| Inadequate Technology Transfer | MNCs may transfer outdated or unsuitable technology to host countries. |
| Environmental Pollution | MNCs can contribute to environmental degradation through their operations. |
| Employment Instability | MNCs may reduce or close manufacturing sites during economic downturns, impacting local employment. |
| Human Rights Abuses | MNCs have been known to prioritize profits over human rights. |
Advantages of Being a Multinational Corporation
Multinational corporations (MNCs) enjoy various benefits. This includes operational efficiency, access to diverse talent and innovation, and favourable tax environments. These advantages, therefore, help MNCs play a significant role in the global economy.
Operational Efficiency
Through their presence in multiple countries, MNCs can work efficiently. They also benefit from lower production costs and being close to their markets. The balance in their operations leads to reduced costs and a stronger bottom line.
Access to Talent and Innovation
Global expansion means MNCs can further tap into a wider talent pool. This lets them draw in top professionals worldwide. It also fosters an environment of constant innovation and creative problem-solving. Their reach also helps them spot and seize new market trends.
Tax and Regulatory Benefits
By strategically placing operations, MNCs can further benefit from various tax and regulatory perks. That is, creating subsidiaries in low-tax regions can save them a lot of money. These companies also enjoy advantages like special economic zones and tax breaks. This leads to better financial performance and more streamlined operations.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | MNCs can leverage their global presence to achieve lower production costs, proximity to target markets, and economies of scale. |
| Access to Talent and Innovation | MNCs can attract and retain top-skilled professionals from around the world, fostering a culture of innovation and creativity. |
| Tax and Regulatory Benefits | MNCs can strategically structure their operations to take advantage of favorable tax and regulatory environments in different countries. |
Challenges Faced by Multinational Corporations
MNCs encounter issues in legal and regulatory, political and economic, and cultural areas. Hence, to operate internationally, MNCs must employ well-thought-out strategies.
Legal and Regulatory Complexities
MNCs deal with a vast array of laws and regulations worldwide. As a result, violating these can bring lawsuits, damage reputation, threaten legitimacy, and may even lead to criminal charges against managers.
Political and Economic Risks
The world’s political and economic climates are often unpredictable. Therefore, MNCs’ success hinges on how well they manoeuvre in these uncertain environments.
Cultural Differences and Adaptation
Managing various cultures is also a critical test for MNCs. They must learn and adopt local customs, values, and ways of communication. This is also necessary to establish trust and beneficial relationships.
To surmount these diverse challenges, MNCs require an approach that integrates legal knowledge, risk assessments, and cultural understanding. They should further enhance their awareness of local laws, adhere to ethical practices, and collaborate with local communities. This approach, therefore, enables MNCs to effectively operate in the global arena and leverage opportunities around the world.
Strategies for Successful Multinational Operations
Multinational corporations (MNCs) face intricate challenges worldwide. Hence, they must adopt strategic techniques to guarantee operational prosperity. Three fundamental strategies at the disposal of MNCs are promoting local cultural immersion and sensitivity, managing risks efficiently, and upholding corporate social responsibility.
Localization and Cultural Sensitivity
To operate across borders effectively, MNCs must deeply comprehend and adjust to diverse cultural expectations in target markets. Entities like Netflix and H. J. Heinz have embraced a multi-domestic strategy. That is, they emphasize meeting each market’s unique needs. Equally, the likes of McDonald’s and KFC maintain their global identities but adapt menus to suit local tastes. The customization of products, marketing, and communication tactics also play a critical role in linking MNCs with local consumers and stakeholders.
Risk Management and Compliance
Dealing with the legal and regulatory maze of numerous countries presents a significant hurdle for MNCs. Hence, they need a sturdy risk management system to tackle challenges like complex tax laws and unstable political environments. They must also implement thorough measures for compliance, including establishing a legal existence locally. This is vital for avoiding legal pitfalls and ensuring the undisturbed progress of their global ventures.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Expanding globally also necessitates a commitment to initiatives that support local communities and address pressing issues. MNCs distinguish themselves by paying superior wages and contributing to the host countries’ economies through taxes. This not only enhances their reputation but also benefits the local economy. Additionally, engaging local workers and tapping into their knowledge promotes innovation and deepens connections within communities.
By skillfully integrating local needs and cultural nuances, managing risks adeptly, and engaging in socially responsible practices, MNCs can effectively navigate the challenges of cross-border operations. This approach aids in achieving sustainable success in the global market.
List of MNCs
Multinational corporations (MNCs) stand as global giants, reaching across borders and significantly shaping the world economy. Found in sectors like technology, food and beverage, automotive, banking, and more, they are some of the leading forces in their fields.
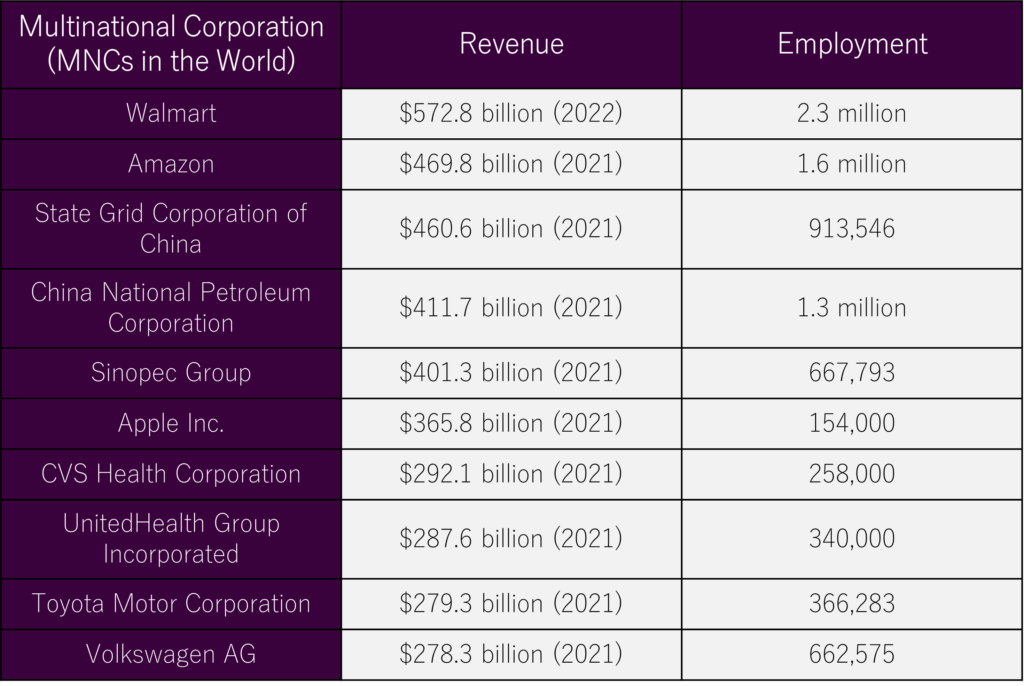
Biggest MNCs in the World
Technology titans including Microsoft, Samsung, and Siemens, and food and beverage leaders like Nestlé, PepsiCo, and Carlsberg, form the elite among MNCs. The automotive arena sees giants such as BMW, Ford, Honda, and Toyota. In banking and finance, the scene is set by Citigroup, HSBC, and JPMorgan Chase.
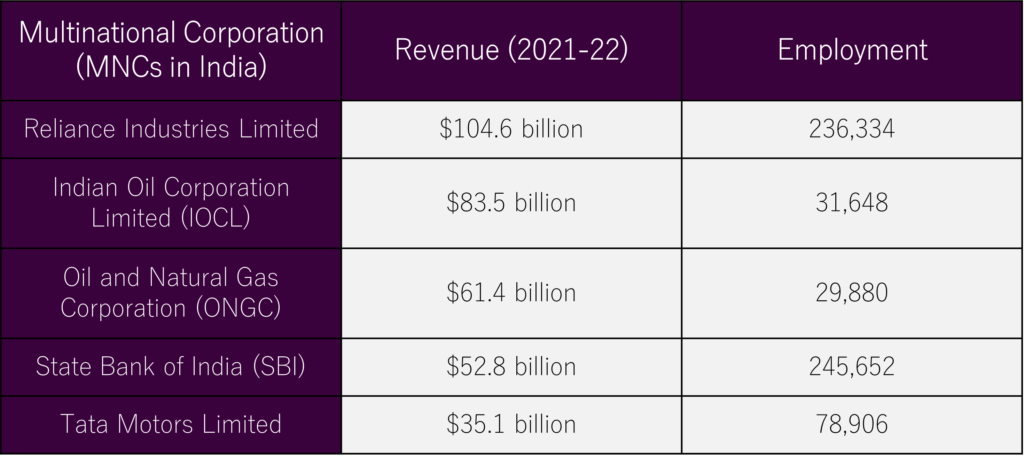
MNCs in India
India hosts prominent MNCs like LTI, TCS, Tech Mahindra, Deloitte, and Capgemini. Also known for their expansive global reach, these companies proliferate their products and services internationally. They stand out for their large turnovers, varied assets, and assertive marketing. Reflecting trends worldwide, MNCs in India have their headquarters domestically and scattered operations globally.
Conclusion
Multinational corporations (MNCs) are, therefore, key players in the global economy, contributing to growth and integration across multiple countries. They utilize their vast international resources and capabilities. This helps them overcome economic challenges, benefiting not just themselves, but the worldwide market. Within this dynamic, MNCs enjoy the advantage of global market access, operational cost savings, and the creation of employment opportunities. Yet, they encounter diverse hurdles like navigating through legal complexities and differing cultural norms.
Their presence significantly influences global trade patterns and economic ties, aligning with the ever-increasing interconnection of nations. Given this trend, the sphere of influence that MNCs wield over the economic stage will undoubtedly amplify. Nevertheless, it is imperative for these entities to prioritize ethical operational standards and support for their employees and the communities they operate within. This ethical balance is vital to their financial goals.
To maintain a competitive edge, MNCs must carefully manoeuvre through a variety of international regulations, political changes, and societal norms. They also must address consumer and stakeholder demands effectively. By laying a foundation of sustainable practices, promoting continual innovation, and forging strong bonds with local communities, MNCs can secure their future success while benefiting the world at large.
Econometrics Tutorials with Certificates
This website contains affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission at no additional cost to you.


